vue-i18next
Internationalization for vue using the i18next i18n ecosystem.
Installation
Source can be loaded via
# npm package
$ npm install @panter/vue-i18next
- If you don't use a module loader it will be added to
window.VueI18next
Requirements
- vue >= 2.0.0
- i18next >= 6.0.1
Usage
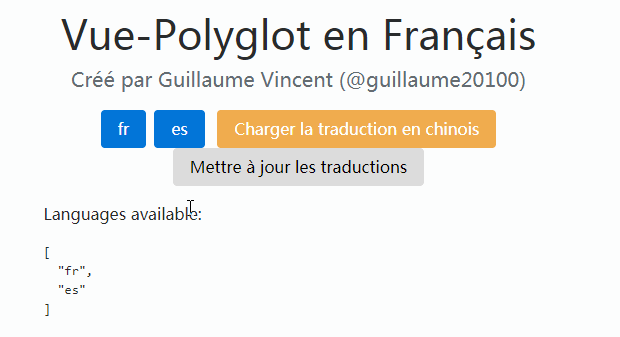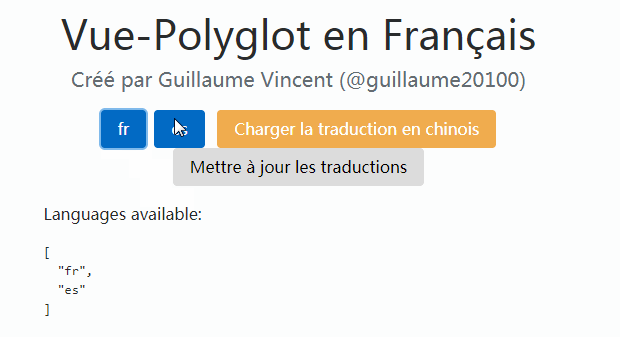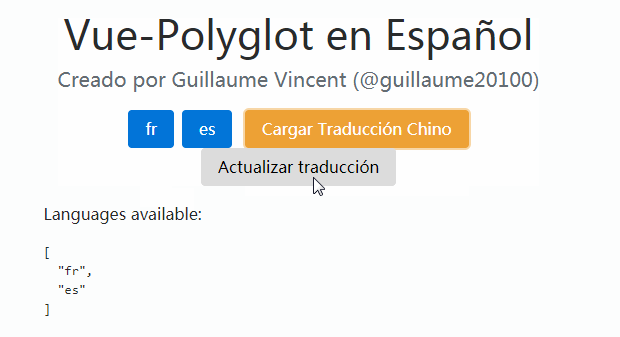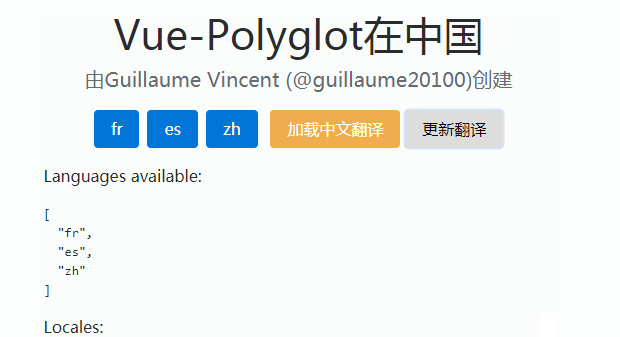
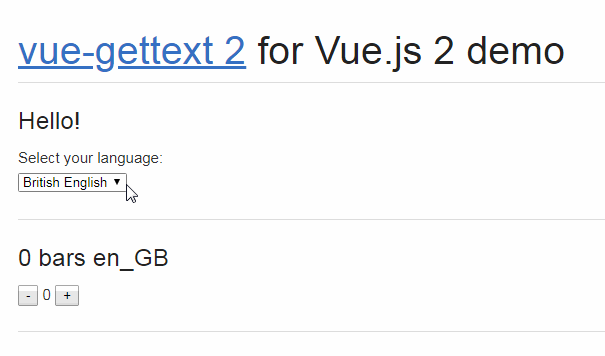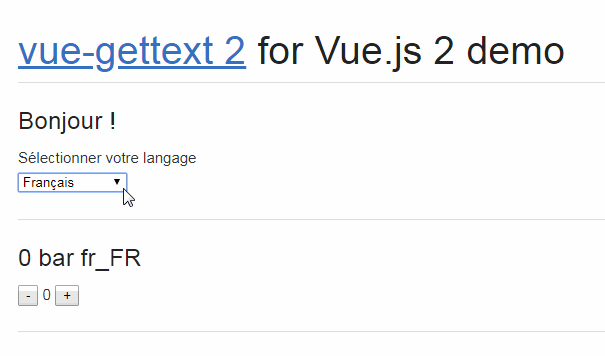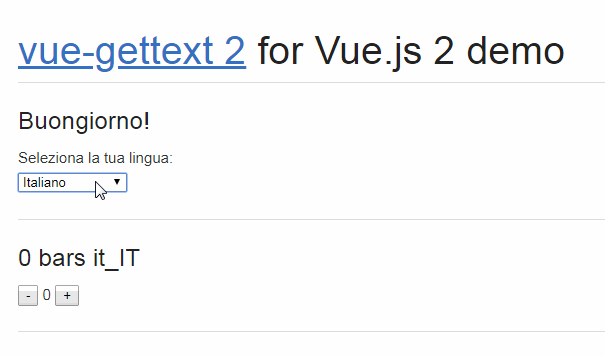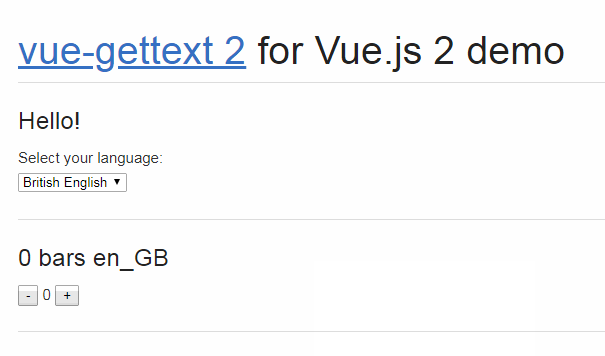
Check the DEMO to see vue-i18next in action.
Init
import Vue from 'vue';
import i18next from 'i18next';
import VueI18Next from '@panter/vue-i18next';
Vue.use(VueI18Next);
i18next.init({
lng: 'de',
resources: {
...
}
});
const i18n = new VueI18Next(i18next);
new Vue({
...
i18n: i18n,
});
Init direct in Browser
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/[email protected]/i18next.js"></script>
<script src="vue-i18next.js"></script>
i18next.init({
lng: "en",
resources: {
en: { translation: locales.en },
de: { translation: locales.de }
}
});
const i18n = new VueI18next(i18next);
new Vue({
i18n
}).$mount("#app");
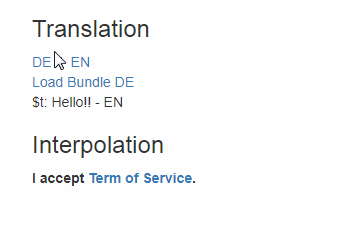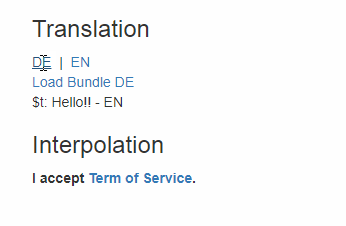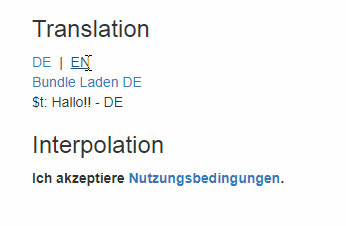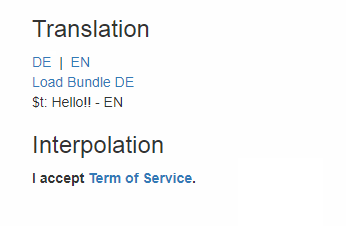
$t
The $t function is a wrapper for i18next.t.
Check i18next documentation for more informations.
const locales = {
en: {
loadbundle: 'Load bundle language: {{lang}}',
}
};
i18next.init({
lng: 'en',
resources: {
en: { translation: locales.en },
},
});
const i18n = new VueI18next(i18next);
Vue.component('app', {
template: `
<div>
<strong>{{$t("loadbundle", {lang: this.lang}) }}</strong>
</div>`,
data() {
return {
lang: 'DE',
};
});
find i18n in the context
Vue.component("language-changer", {
template: "<div><a v-on:click=\"changeLanguage('de')\">DE</a></div>",
methods: {
changeLanguage(lang) {
this.$i18n.i18next.changeLanguage(lang);
}
}
});
Change Language
import i18next from 'i18next';
...
i18next.changeLanguage('it');
Component interpolation
const locales = {
en: {
tos: "Term of Service",
term: "I accept {{0}}. {{1}}.",
promise: "I promise"
}
};
i18next.init({
lng: "en",
resources: {
en: { translation: locales.en }
}
});
const i18n = new VueI18next(i18next);
Vue.component("app", {
template: `
<div>
<i18next path="term" tag="label">
<a href="#" target="_blank">{{ $t("tos") }}</a>
<strong>{{ $t("promise") }}</strong>
</i18next>
</div>`
});
Directive
Full Featured properties:
path: stringlanguage: language, optionalargs: object
const locales = {
en: {
hello: "Hello",
helloWithName: "Hello {{name}}"
}
};
i18next.init({
lng: "en",
resources: {
en: { translation: locales.en }
}
});
const i18n = new VueI18next(i18next);
// simple usage
Vue.component("app", {
template: `<p v-t="hello"></p>`
});
// full featured
Vue.component("app", {
template: `<p ref="text" v-t="{ path: 'helloWithName', language: 'en', args: { name: 'Hans' } }"></p>`
});
i18nOptions
The namespace will be loaded with (loadNamespaces)[http://i18next.com/docs/api/#load-namespaces],so one can lazy load namespaces for components.
const locales = {
en: {
tos: "Term of Service",
term: "I accept {{0}}. {{1}}.",
promise: "I promise"
}
};
i18next.init({
lng: "en",
fallbackLng: "en",
resources: {
en: { common: locales.en }
}
});
const i18n = new VueI18next(i18next);
Vue.component("app", {
i18nOptions: { namespaces: "common" },
template: `
<div>
<i18next path="term" tag="label">
<a href="#" target="_blank">{{ $t("tos") }}</a>
<strong>{{ $t("promise") }}</strong>
</i18next>
</div>`
});
There is also the possibility to prefix what key the component is using.
const locales = {
en: {
message: {
hello: "Hello"
},
}
};
i18next.init({
...
});
const i18n = new VueI18next(i18next);
Vue.component('app', {
i18nOptions: { keyPrefix: 'message'},
template: `
<div>
<strong>{{ $t("hello") }}</strong>
</div>`,
});
Translations can not only be defined in translation files but also in the i18nOptions.
i18next.init({
...
});
const i18n = new VueI18next(i18next);
Vue.component('app', {
i18nOptions: {
messages: {
de: {
hello: 'Hello!'
}
}
},
template: `
<div>
<strong>{{ $t("hello") }}</strong>
</div>`,
});
Single file components
by @kazupon
<i18n>
{
"en": {
"hello": "hello world!"
}
}
</i18n>
<template>
<div id="app">
<p>message: {{ $t('hello') }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'app',
}
</script>
To be able to use the <i18> you need to use the vue-loader:
npm install @kazupon/vue-i18n-loader --save-dev
module.exports = {
// ...
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.vue$/,
loader: 'vue-loader',
options: {
loaders: {
// you need to specify `i18n` loaders key with `vue-i18n-loader` (https://github.com/kazupon/vue-i18n-loader)
i18n: '@kazupon/vue-i18n-loader'
}
}
},
// ...
]
},
// ...
}
Use it with YAML:
npm install yaml-loader --save-dev
<i18n>
en:
hello: "hello world!"
</i18n>
module.exports = {
// ...
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.vue$/,
loader: "vue-loader",
options: {
preLoaders: {
i18n: "yaml-loader"
},
loaders: {
i18n: "@kazupon/vue-i18n-loader"
}
}
}
// ...
]
}
// ...
};
Use Vue.Filter to deal with empty keys
by: @Fohlen
Vue.filter("t", value => {
if (!value) return "";
return i18n.t(value);
});
Usage:
{{ $t('some_text') }}
{{ 'some text' | t }}
Build Setup
# install dependencies
yarn install
# serve with hot reload at localhost:8080
yarn run dev
# build for production with minification
yarn run build