Vuetify-Form-Base
Imagine you get the following data in JSON format and have to edit it now.
{
prename: 'Will',
name: 'Smith',
retired: false
adresses: [
{
street:'Time Square',
city: 'New York',
country: 'US'
},
{
street:'Champs Elysee',
city: 'Paris',
country: 'FR'
}
]
}
Normally you have to flatten the data structure and then map it to an appropriate form. Then you have to define the form in HTML and animate it with your data.
With Formbase you create a JSON Object with the same structure which describes your form.
You have to create a lot of different Forms? You have to manipulate or edit Data presented in JS-Objects?
Then give Vuetify-Form-Base a Try. This Schema-based Form Generator is a Vue.js 2.0 Component and can simplify your Job by automatically creating full editable Forms. Edit this Forms and get reactive Results.
Vuetify-Form-Base uses the well known Component Framework Vuetify to style and layout your Form. Vuetify Controls have a clear, minimalistic design, and support responsive Design.
Demo
or
Download Project, change current directory to ../vuetify-form-base/example and then run
npm install
npm run serve
Intro
vuetify-form-base is a Vue Component and can easily integrated into any Vue Project.
The Schema-Object has the same structure as the Value-Object. Create a Schema by cloning the Value-Object and replace the Values of the Data-Object by Definitions for your your Schema. The corresponding Schema-Object defines type, layout and functional behaviour of your Form.

The Component Framework Vuetify styles your Form. The Controls have a clear design, but don't worry you can change your style in a lot of ways. For more details see section Style with CSS
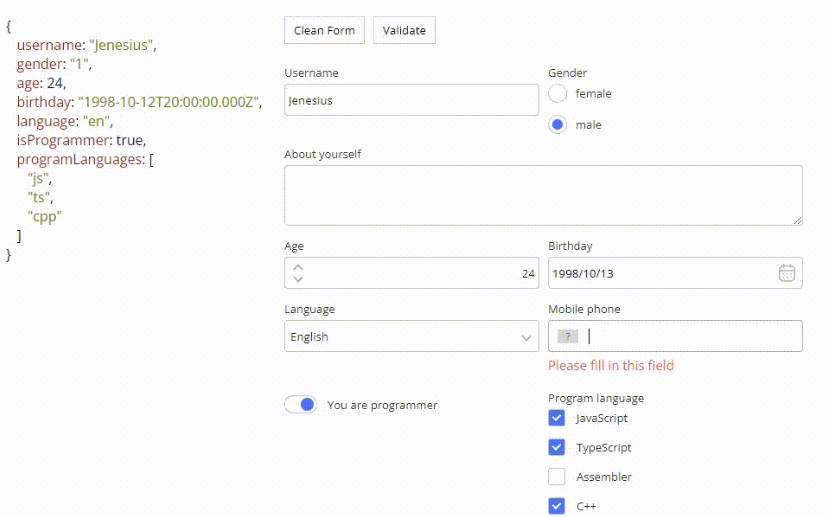
Based on an existing Value-Object vuetify-form-base generates a full editable Form.
Layout and Functionality are defined in a Schema-Object, which has the same Property structure as the Value-Object. Your Data-Object keeps full reactive and any Input or Change in your Form triggers an Event too. If you have a deep nested Value-Object or an Array -Structure you can direct work on it. There is no need to flatten or modify your Data-Presentation.
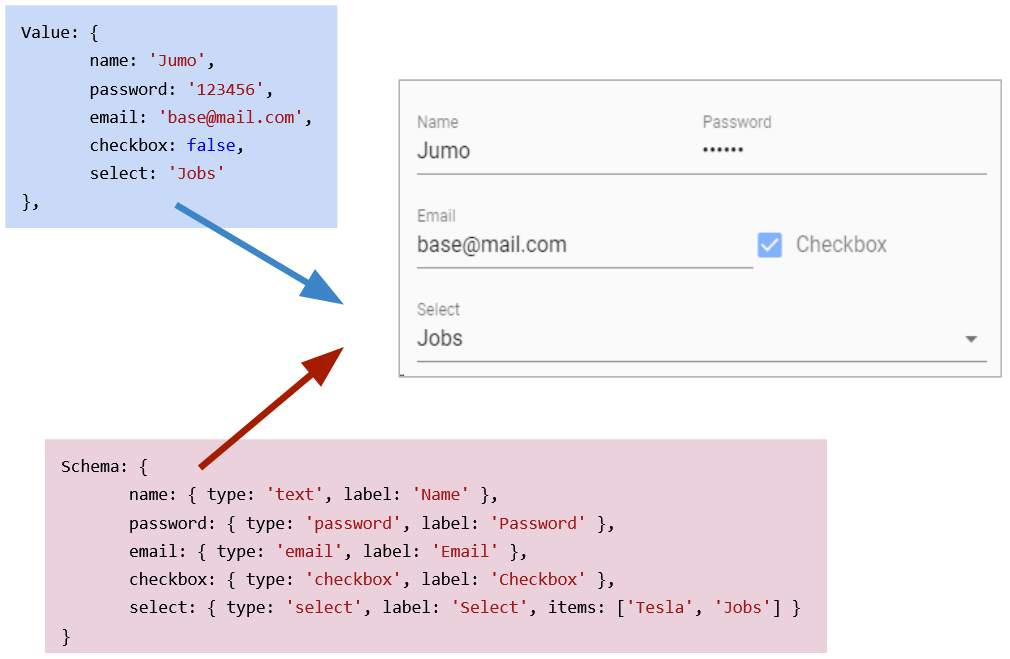
Changing any Field in the Form gives you a reactive Result in your Value-Object.
Furthermore you can synchronize two or more Forms by using same Value-Object.
If you want a Partial-Form which displays only parts of your Data.Object, then link a property of your Data-Object to your vuetify-form-base Component.
And if necessary you can also build a Form in Form by using Slots.
Use the v-on directive of Vue.js to listen to Formbase triggered Events for 'Resize', 'Focus', 'Input', 'Click' and 'Swipe'. Listening to 'Update' will catch all Events.
Select from Vuetify UI Input & Controls like Textfield, Password, Email, Textarea, Checkbox, Radio, Switches, Sliders, Combobox, Autocomplete, Select, Combobox, Date- or Timepicker and some other fields.
More Informations to Vuetify Textfields find here.
Installation
For proper working you need a Vue.js Project with Vuetify installed. For more Details see Vuetify Quickstart.
npm install vuetify-form-base --save
vuetify-form-base is a Vue.js single-file component with a .vue extension and you can use it like any Vue-Component.
In order for your application to work properly, you must wrap it in a v-app component. This component is required and can exist anywhere inside the body, but must be the parent of ALL Vuetify components. v-content needs to be a direct descendant of v-app.
<template>
<v-app>
<v-content>
<v-container fluid>
<v-form>
<v-form-base :value="myValue" :schema="mySchema" />
</v-form>
</v-container>
</v-content>
</v-app>>
</template>
import VFormBase from 'vuetify-form-base';
export default {
components:{ VFormBase },
data () {
return {
myValue: {
name: 'Jumo',
password: '123456',
email: '[email protected]',
checkbox: true,
select: 'Jobs',
},
mySchema: {
name: { type: 'text', label: 'Name' },
password: { type: 'password', label: 'Password' },
email: { type: 'email', label: 'Email' },
checkbox: { type: 'checkbox', label: 'Checkbox' },
select: { type: 'select', label: 'Select', items: ['Tesla', 'Jobs', 'Taleb'] }
}
}
}
}
and you will get a full editable Form based on your schema and filled with your Value-Object.
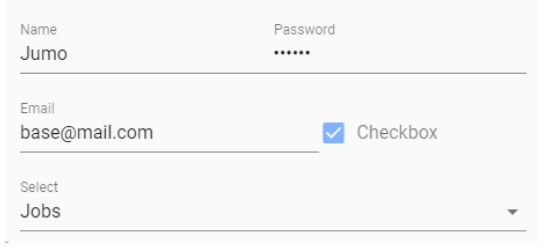
INFORMATION:
Properties in 'myValue' without corresponding Prop in 'mySchema', are ignored and keep untouched, but a initial warning will be logged to console
Example with nested Object
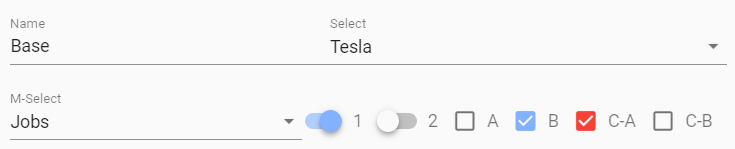
In Reality sometimes you will have deep nested objects or arrays, which should be edited. vuetify-form-base works for you and flatten internally this nested object and build a plain Form.
myValue: {
name: 'Base',
controls:{
selection:{
select: 'Tesla',
selectM: ['Jobs'],
},
switch: [ true,false ],
checkbox: [ false, true, {
checkboxArray: [ true, false ]}
]
}
},
mySchema: {
name: { type: 'text', label: 'Name'},
controls:{
selection:{
select: { type: 'select', label: 'Select', items: ['Tesla', 'Jobs', 'Taleb'] },
selectM: { type: 'select', label: 'M-Select', multiple:true, items: ['Tesla', 'Jobs', 'Taleb']}
},
switch: [
{ type: 'switch', label: '1' },
{ type: 'switch', label: '2' }
],
checkbox: [
{ type: 'checkbox', label: 'A' },
{ type: 'checkbox', label: 'B' },
{ checkboxArray: [
{ type: 'checkbox', label: 'C-A', color:'red' },
{ type: 'checkbox', label: 'C-B', color:'red' }
]}
],
}
}
Computed Schema
IF you want Schema Properties to be changed dynamic, then you must make your Schema Object a computed property. This Example turns the Radio Layout from Column to Row on Resizing to medium Size or greater.
data () {
return {
myValue: {
radio: 'A',
}
}
},
computed: {
mySchema(){
return {
radio: { type: 'radio', row: this.row, options:['A','B'] }
}
},
row () {
return this.$vuetify.breakpoint.mdAndUp
}
},
Vuetify Layout and Grid
Integrate Vuetify Grid by using the Schema-Properties 'flex', 'offset' and 'order':
mySchema: {
name: { type: 'text', flex: 4, offset: 2, order: 1 },
}
flex: 4 // shorthand for flex: { xs:4 }
offset: 2 // shorthand for offset: { xs:2 }
order: 1 // shorthand for order: { xs:1 }
A more responsive Solution with 'flex', 'offset' or 'order' needs an Object as Value. For more Details see Vuetify Documentation:
Vuetify - Grid:
flex: { xs:12, sm:8, md:6, lg:4 }
Vuetify - Offset:
offset: { xs:0, sm:1, md:2, lg:2 }
Vuetify - Order:
order: { xs:1, sm:1, md:2, lg:2 }
Link & Synchronize
Forms can be linked together using the same Value-Object. Changes in one Form are synchronized and reflected in the other Form.
<v-form-base :value="myValue" :schema="mySchema" />
<v-form-base id="form-sync" :value="myValue" :schema="mySchema" />
Vuetify Controls API-Props
Vuetify Controls have a API with Props These Props in Vuetify-Controls comes in kebab-case amd must for use in Schema-Object converted to CamelCase
<!-- vuetifyjs.com -->
Input & Controls
Text-fields
API-Props
append-icon
background-color
<!-- JS -->
mySchema: {
name: { type:'text', appendIcon:'menu', backgroundColor': 'red' },
...
}
Schema
<form-base :schema="schema" ... />
Schema is an JS-Object, which defines and controls the behavior of your Form. Each Key Prop) in your Schema-Object must reflect a Key from your Data-Object. A minimalistic Definition of a text input could look like this:
schema:{
name: { type:'text'}
}
The next shows a more complex Schema:
// Partials Functions for Rules
const minLen = l => v => (v && v.length >= l) || `min. ${l} Characters`
const maxLen = l => v => (v && v.length <= l) || `max. ${l} Characters`
const required = msg => v => !!v || msg
const validEmail: msg => v => /.+@.+\..+/.test(v) || msg
// Destruct Value and return a Value!
const toUpper = ( {value} ) => value && value.toUpperCase()
export default {
components: { VFormBase },
data () {
return {
myValue: {
name: 'Base',
password: '123456',
email: '[email protected]'
},
mySchema: {
name: {
type: 'text',
label: 'Name',
hint:'Converts to UpperCase'
toCtrl: toUpper,
fromCtrl:toUpper,
rules: [ required('Name is required<>) ]
flex: 12,
},
password: {
type: 'password',
label: 'Password',
hint:'Between 6-12 Chars',
appendIcon: 'visibility',
counter: 12,
rules: [ minLen(6), maxLen(12) ],
clearable: true,
flex: 12
},
email: {
type: 'email',
label: 'Email',
rules: [ validEmail('No valid Email'), required('Email is required<>) ],
flex: 12
}
}
}
}
}
Available Properties in Schema
For further Props see Vuetify Controls API
schema:{
type: string // text, password, email, radio, switch, slider,
// combobox, autocomplete, select, combobox, date, time, ...
sort: N // use simple order to display items
order: N or Object // use Vuetify-Grid to order items responsive
flex: N or Object // See Vuetify Grid
offset: N or Object // See Vuetify Grid
label string, // label of item
placeholder: string, // placeholder
hint: string, // additional Info
color: string
backgroundColor:string
css: string, // inject classnames - schema:{ name:{ css:'small'}, ... }
mask: string, // regex to control input
multiple: bool, // used by type: select, combobox, autocomplete
required: bool, // need an input value
hidden: bool, // hide item - set from another item
disabled: bool,
readonly: bool,
appendIcon: icon // click triggers event with icon-location
prependIcon: icon // click triggers event with icon-location
items: array // ['A','B'] used by type: select, combobox, autocomplete
options: array, // ['A','B'] used by type:radio
rules: array of Fn // [ value => true || false, ... ]
// must return a (modified) value!!
toCtrl: function, // ( {value, obj, data, schema} ) => value
fromCtrl: function, // ( {value, obj, data, schema} ) => value
}
Events
We can use the v-on directive to listen to vuetify-form-base events 'focus', 'input', 'click', 'resize', 'swipe', 'update' and run some Code when they’re triggered.
This Example use the Default ID and listen all events with 'update':
<!-- HTML -->
<v-form-base :value= "myValue" :schema= "mySchema" @update= "updateCode" />
This has a Custom ID and listen all events in separate methods. Your v-on Directive must append the Custom ID:
<!-- HTML -->
<v-form-base
id = "form-base-complex"
:value= "myValue"
:schema= "mySchema"
@resize:form-base-complex= "resizeCode"
@focus:form-base-complex= "focusCode"
@click:form-base-complex= "clickCode"
@swipe:form-base-complex= "swipeCode"
@input:form-base-complex= "inputCode"
/>
The Event-Signature:
{ on, id, key, value, obj, event, params, size, data, schema }
on - Trigger Name // focus | input | click | resize | swipe or update to listen all
id - Formbase-ID
key - key of triggering Element
value - value of triggering Element
obj - triggering Element { key, value, schema }
params - params object if available { x, y, pos, icon }
event - the native trigger-event if available
data - Data-Object
schema - Schema-Object
Use 'Update' Event to control Visibility of Password Element
<!-- HTML -->
<v-form-base :value="myValue" :schema="mySchema" @update="update">
<!-- JS -->
update ({ on, id, key, value, obj, event, params, size, data, schema }) {
console.log('[ on, key, value, params]', on, key, value, params )
// is 'click' and comes from appendIcon on key 'password'
if (on == 'click' && key == 'password' && (params && params.pos) == 'append') {
// toggle icon
obj.schema.appendIcon = obj.schema.type === 'password'
? 'lock'
: 'visibility'
// toggle visibility
obj.schema.type = obj.schema.type === 'password'
? 'text'
: 'password'
}
}
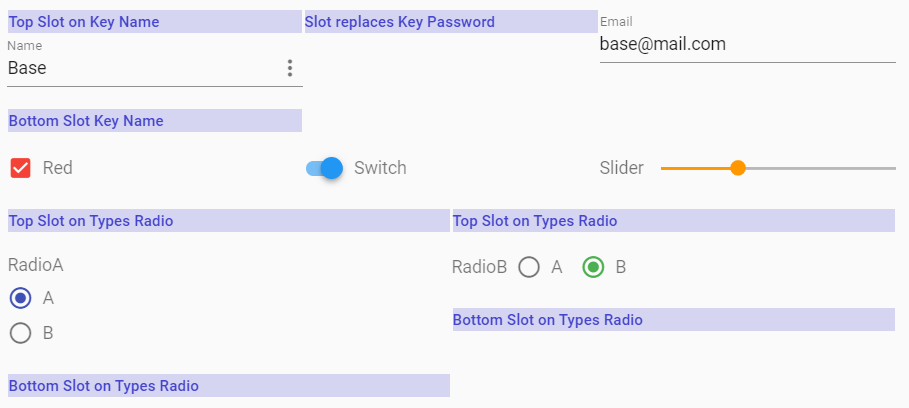
Slots
Use Slots to pass Header and Footer into a Control. If necessary replace Controls by Slots. Any slot could be a v-form-base component itself.
<v-form-base :value="myValue" :schema="mySchema" @update="update">
<h4 slot="slot-top-key-name">Top Slot on Key Name</h4>
<h4 slot="slot-top-type-radio">Top Slot on Types Radio</h4>
<h4 slot="slot-item-key-password">Slot replaces Key Password</h4>
<h4 slot="slot-bottom-key-name">Bottom Slot Key Name</h4>
<h4 slot="slot-bottom-type-radio">Bottom Slot on Types Radio</h4>
</v-form-base>
Form Validation
If you need Form Validation you have to wrap v-form-base with v-form and take the reference of v-form for working on.
<!-- HTML -->
<v-form ref="form" v-model= "formValid" lazy-validation>
<v-form-base :value= "myValue" :schema= "mySchema" @update= "update"/>
</v-form>
<!-- JS -->
validate () {
this.$refs.form.validate()
},
resetValidation () {
this.$refs.form.resetValidation()
},
Style with CSS
Customize your vuetify-form-base component using CSS-Classnames
IMPORTANT:
Don't use<style scoped>in parents component, because scoped definitions
are inside the child component not accessable
Formbase - ID
#form-base is the default ID of your component. If you need different CSS for two or more forms in the same parent component, then change default value by setting a different ID for each component and use this new ID. Using a 'custom-id' you have to modify the event-binding to @update:custom-id = "update"
<!-- Default ID CSS-Style -->
#form-base {...}
<!-- HTML-Template -->
<v-form-base @update= "update" />
<!-- Custom-ID CSS-Style -->
#custom-id {...}
<!-- HTML-Template -->
<v-form-base id="custom-id" @update:custom-id= "update" />
General - Classname
#form-base {...}
Type - Classnames
Style all items of a specific type, then use type specific classnames. They start with type- appended by any type. You can use following types in your Schema-Object:
'text', 'email', 'password', 'textarea', 'select', 'autocomplete', 'combobox', 'radio', 'checkbox', 'slider', 'switch', 'date', 'time'
#form-base .type-text { color: #44A }}
#form-base .type-email { font-weight:500; }
Key - Classnames
Set Classname of deep key in your Data-Object, by converting .dot notation 'person.adress.city' into kebab case 'person-adress-city' prepending 'key-'
<!--
myValue{ person:{ adress:{ city:'',... } ... } ... }
CSS Classname to access to key 'city'
-->
#form-base .key-person-adress-city { font-weight:500; }
<!--
Access to myValue: { name:'' }
CSS Classname to access key 'name'
-->
#form-base .key-name { font-weight:500; }
<!--
myValue: { controls: { slide: [25, 64] }
Access First Entry in Array of Key Slide
-->
#form-base .key-controls-slide-0 { font-weight:500; }
Validate with Pseudoselectors
#form-base .item input:valid { background-color: #afa; }
#form-base .type-email input:invalid { background-color: #faa; }
#form-base .key-name input:focus { background-color: #ffd; }
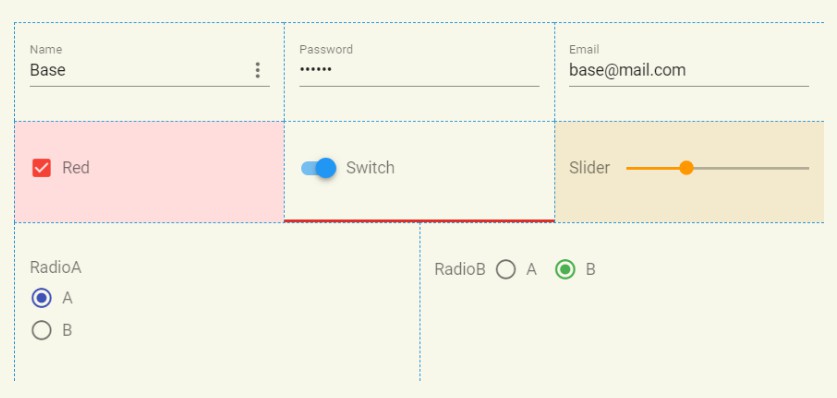
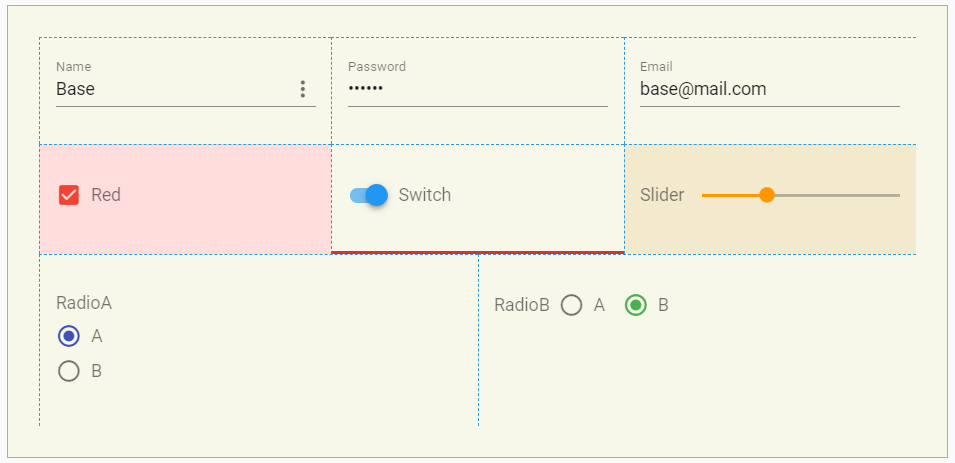
CSS - Example
<!-- JS -->
myValue: {
name: 'Base',
password: '123456',
email: '[email protected]',
controls: {
checkbox: true,
switch: true,
slider: 33,
radioA: 'A',
radioB: 'B'
}
}
<!-- CSS -->
<style>
#form-base {
border: 1px solid #cb2;
background-color: #ffe;
padding:2rem
}
/* CSS Item --- set all items */
#form-base .item {
border-left: 1px dashed #29D;
border-top: 1px dashed #29D;
padding:1rem
}
/* CSS Type --- set all items with type */
#form-base .type-switch { border-bottom: 3px solid #E23}
#form-base .type-checkbox { background-color: #fdd }
/* CSS Keys --- select key in object 'myValue.controls.slider' */
#form-base .key-controls-slider { background-color: #fec }
</style>
Features
- Vue-Component
- integrates UI framework Vuetify with responsive Layout and Support of Grid
- Use a lot of Vuetify Control & Input types inclusive available API-Props
- Get full configurable Forms based on Schema Definition
- Edit plain or deep nested objects including Arrays, without the Need to flatten it
- Get a Full reactive Result
- Listen on 'Resize', 'Focus', 'Input', 'Click', 'Swipe' and 'Update' Events
- Use Slots to pass Header and Footer into a Control. Or replace a Control by Slot
- Configurable CSS Style
Dependencies
Vue >= 2.4
Vuetify >= 1.4
Lodash > 4.0