vuensight ?
Visualize Vue.js component relationships and communication channels, i.e. props, events and slots. This tool operates on the command line and is made for developers. The aim of vuensight is to provide visual insight into the components of a Vue.js project and to support developers before and during refactoring, e.g. by visually analyzing which prop is used in which parent component or by highlighting unused components or channels.
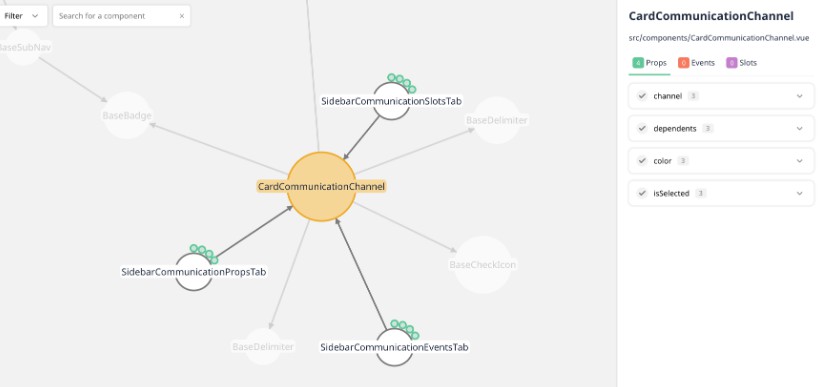
An example visualization of vuensight itself:

This tool is built on top of the two awesome packages:
- dependency-cruiser for building the dependency tree
- vue-docgen-api for parsing the Vue files
Getting started ?
Install
First install the cli tool locally in the project you want to visualize:
npm i -D @vuensight/cli
Or globally on your machine if you plan to visualize multiple projects:
npm i -g @vuensight/cli
Run in project
Then run the tool in your project folder (local install):
npx vuensight
or if you installed vuensight globally:
vuensight
Options
--diror-d(optional): Specify the directory that should be parsed relative from your current working directory, default issrc--webpack-configor-wpc(optional): Specify the path to your webpack-config (from your current working directory). This is particularly important if you use aliases.--ts-configor-tsc(optional): Specify the path to your TypeScript config file (from your current working directory).
An example usage:
npx vuensight --dir resources/js --webpack-config ./webpack-config.json --ts-config ./tsconfig.json
Licencse
Development
Requirements
npm version >= 7(the project is a monorepo and uses npm workspaces which require at least npm version 7)
Installing dependencies
npm i(in root directory) to install all dependencies of all packagesnpm i <package-name>to add a global dependency for all packagesnpm i <package-name> --workspace @vuensight/<vuensight-package-name>to add a new dependency to a specific package
Build packages
npm run buildin root folder (to build all packages at the same time)npm run buildin each package
Build watcher
npm run build:watchin every package separately
Unit tests
npm run testin root (to run tests for all packages)npm run testin each package
Publish
npm publishin each package